May is Mental Health Awareness Month
in Local Events, Local News, Massachusetts News, National News

May is Mental Health Awareness Month

May is recognized as Mental Health Awareness Month to shine a spotlight on the significance of mental health and the importance of destigmatizing conversations around it. Established in 1949 by Mental Health America, this month serves as an opportunity to educate people about mental illnesses, provide resources for those struggling, and advocate for policies that support mental health care access.
Mental health conditions affect millions of individuals worldwide, yet stigma and misinformation often prevent people from seeking help. By dedicating a month to raising awareness, we create space for conversations about the realities of mental health challenges—emphasizing that it’s okay to ask for help and that recovery is possible.
This month encourages individuals to reflect on their own mental well-being and prioritize self-care. It also inspires communities to come together to support one another, whether by hosting educational events, fundraising for mental health services, or simply reaching out to friends and loved ones to show that they care.
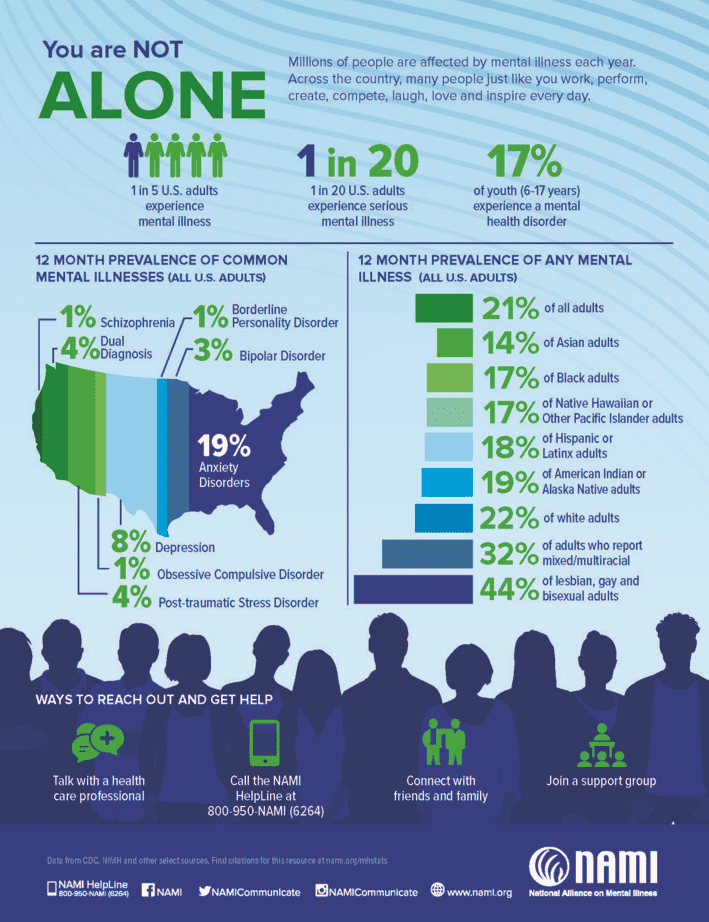
Common Mental Health Disorders
Mental health challenges can vary widely in their nature and impact, but some common ones include:
- Anxiety Disorders: This includes generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety, and specific phobias. Anxiety disorders involve excessive fear or worry that interferes with daily life
- Depression: A mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities.
- Bipolar Disorder: This condition involves extreme mood swings, including emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression).
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Often resulting from a traumatic event, PTSD can cause flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety, among other symptoms.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): A disorder characterized by unwanted, persistent thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) performed to ease the distress caused by those thoughts.
- Eating Disorders: These include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder, and they are marked by unhealthy preoccupations with food, weight, and body image.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Commonly diagnosed in childhood, ADHD affects focus, impulsivity, and organizational skills, and it can continue into adulthood.
- Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders: Conditions that affect how a person thinks, feels, and perceives reality, often including hallucinations and delusions.
- Substance Use Disorders: Addiction to drugs or alcohol, often intertwined with mental health issues, can severely impact mental well-being.
- Personality Disorders: These include conditions like borderline personality disorder (BPD) and antisocial personality disorder, which affect how people think, feel, and behave in relationships.